|
|
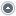
Coaxial cable is a cable consisting of an inner conductor,
surrounded by a tubular insulating layer typically made
from a flexible material with a high dielectric constant,
all of which is then surrounded by another conductive
layer (typically of fine woven wire for flexibility, or of a thin metallic foil), and then finally covered again with a thin insulating layer on the outside. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis.
Coaxial cables are often used as a transmission line for radio frequency signals. In a hypothetical ideal coaxial cable the electromagnetic field carrying the signal exists only in the space between the inner and outer conductors. Practical cables achieve this objective to a high degree. A Coaxial Cable provides protection of signals from external electromagnetic interference, and effectively guides signals with low emission along the length of the cable.
The insulator surrounding the inner conductor may be solid plastic, a foam plastic, or may be air with spacers supporting the inner wire. The properties of dielectric control some electrical properties of the coaxial cable.
Coaxial Cable has braided copper wire forming the shield. Sometimes the braid is tin plated. For better shield performance, some coaxial cables have two or even more shield layers. The shield might be just two braids, but it is more common now to have a thin foil shield covered by a wire braid.
|
Multi-Coaxial Cable
|

 Coaxial Cable
Coaxial Cable